Efficacy and Safety of Long-Term Baricitinib With and Without Methotrexate for the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis: Experience With Baricitinib Monotherapy Continuation or After Switching From Methotrexate Monotherapy or Baricitinib Plus Methotrexate.
Fleischmann R,
Takeuchi T,
Schiff M,
Schlichting D,
Xie L,
Issa M,
Stoykov I,
Lisse J,
Martinez-Osuna P,
Rooney T,
Zerbini CAF
Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 2020;72(8):1112-1121
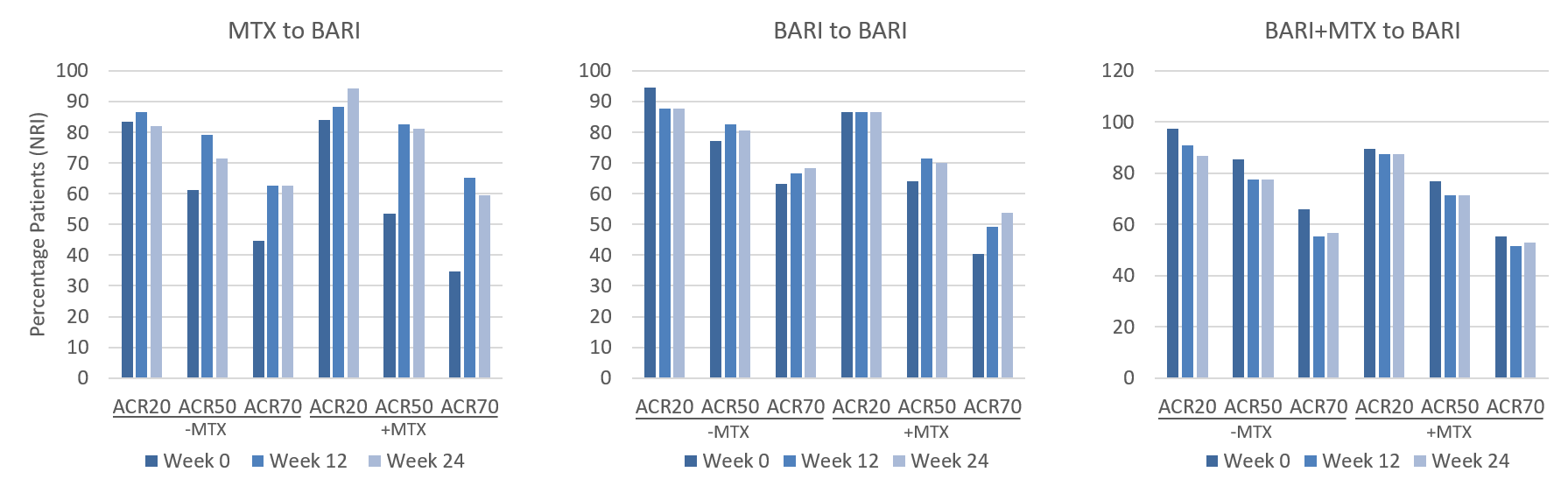
This 24-week update from the baricitinib RA-BEYOND LTE study follows patients previously treated in the pivotal study RA-BEGIN. It demonstrates the maintained safety and efficacy of baricitinib monotherapy, and the effects of concurrent MTX treatment on response rates and patient reported outcomes. Previous P3 study RA-BEGIN demonstrated the superior efficacy of 4mg baricitinib compared to MTX monotherapy up to 52 weeks, with no major safety events being identified. At the end of the trial, patients had the option of continuing treatment in the study RA-BEYOND, with 4mg baricitinib monotherapy being prescribed to all patients starting the trial. RA-BEYOND demonstrated that many patients could maintain baricitinib monotherapy through RA-BEGIN and up to week 24 of the following LTE study. MTX prescription in addition to baricitinib was seen to be greatest during the first 4 weeks of the study, subsequently ‘rescuing’ patients and maintaining responses through to week 24. Generally, patients also showed the greatest within-group improvements in disease activity and function when combining baricitinib therapy with MTX. Overall, the most common TEAEs were noted to be infections and infestations. The most frequently reported of these were nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract and urinary tract infections.