Skeletal muscle effects of Janus kinase inhibition in rheumatoid arthritis (RAMUS): a single-arm, experimental medicine study
Rheumatology 2025 Epub ahead of print doi: 10.1016/S2665-9913(25)00184-5
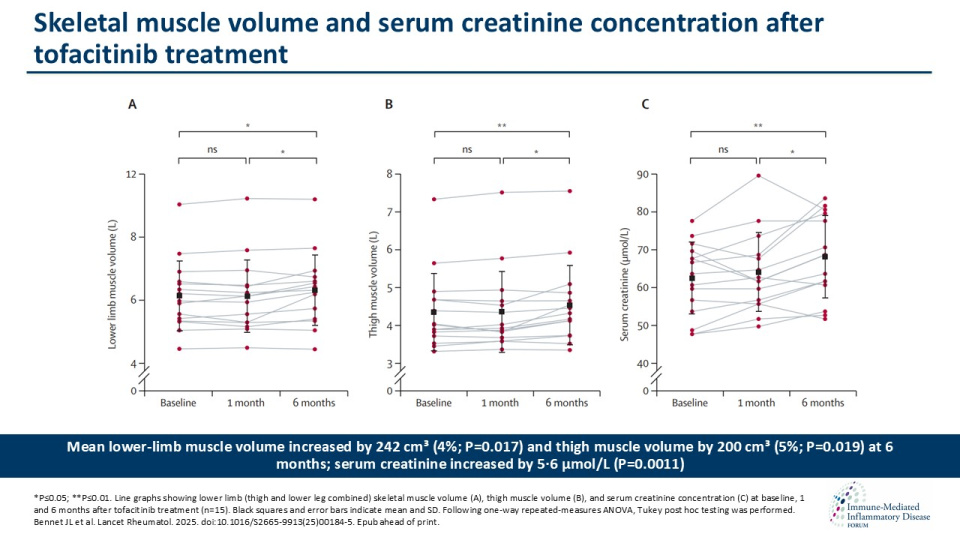
Bennett et al, showed that tofacitinib treatment in adults with rheumatoid arthritis led to a significant increase in lower limb and thigh muscle volume, accompanied by rises in serum creatinine without evidence of renal impairment.
The RAMUS study investigated whether the tofacitinib affected lower limb muscle volume, muscle strength, function, serum biomarkers, and skeletal muscle gene expression. Muscle strength did not significantly improve, but transcriptomic changes suggested reduced interferon-related signalling and enhanced extracellular matrix pathways.