The active metabolite of spleen tyrosine kinase inhibitor fostamatinib abrogates the CD4+T cell-priming capacity of dendritic cells
Rheumatology (Oxford). 2015;54(1):169–177
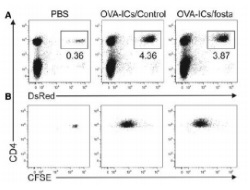
In these murine studies, investigators sought to gain an understanding of how the active metabolite of fostamatinib, R406, affects the inflammatory response at the cellular level, by studying the effects of fostamatinib on antigen-specific interactions between dendritic cells (DC) and CD4+ T cells.
There are several key rheumatology findings from this study; fostamatinib fails to block CD4+ T cell priming in response to immune complexes; R406 inhibits DC stimulatory capacity; CD4+ T cells primed with R406-treated DCs fail to undergo proliferation or functional maturation.
The authors speculate that some of the in vitro effects may be translated in vivo if the correct locale and concentration can be achieved.